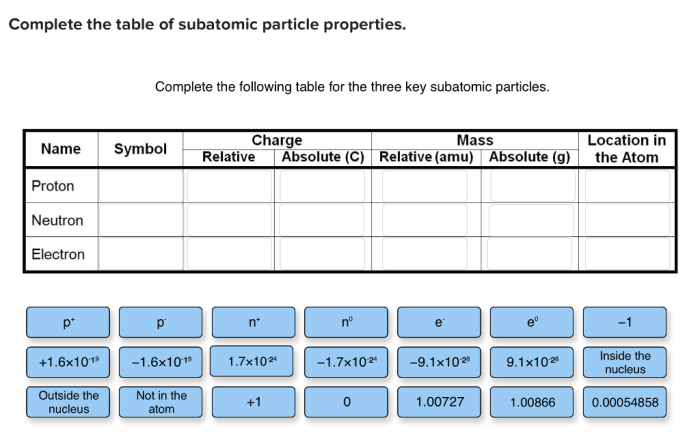
Complete the following table for the three key subatomic particles – Embark on a journey to unravel the fundamental properties of subatomic particles, the building blocks of our universe. This exploration begins with a focus on the three key subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Join us as we delve into their structure, charge, mass, and location within the atom, completing a comprehensive table that unveils the secrets of these microscopic wonders.
As we delve deeper, we will uncover the intricate relationships between these properties and the behavior of subatomic particles. These insights will empower us to identify and classify these particles, providing a deeper understanding of the fundamental forces that shape our world.
Fundamental Properties of Subatomic Particles
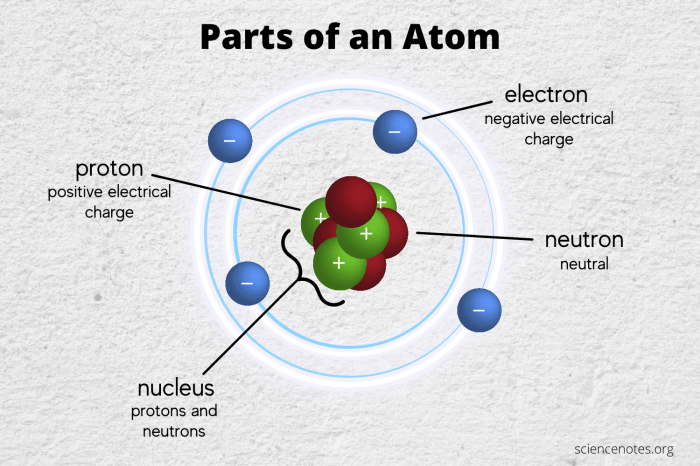
Subatomic particles, the fundamental building blocks of matter, possess unique and defining properties that shape their behavior and interactions within atoms. These properties include charge, mass, and spin.
Charge:Subatomic particles can have a positive, negative, or neutral charge. The charge determines the particle’s attraction or repulsion to other charged particles. Protons carry a positive charge, electrons carry a negative charge, while neutrons are neutral.
Mass:Mass is a measure of the particle’s inertia. It determines the particle’s resistance to changes in motion. The mass of subatomic particles is typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu), with protons and neutrons having approximately equal masses of 1 amu, while electrons have a much smaller mass of approximately 0.00055 amu.
Spin:Spin is a fundamental property of subatomic particles that describes their intrinsic angular momentum. Spin can be either clockwise or counterclockwise, and it influences the particle’s magnetic properties and interactions with other particles.
Key Subatomic Particles: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Within the atom, three key subatomic particles play crucial roles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Protons:Protons are positively charged particles located in the nucleus of the atom. They determine the atomic number of an element and contribute to the mass of the atom.
Neutrons:Neutrons are neutral particles also located in the nucleus. They contribute to the mass of the atom but have no net charge.
Electrons:Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in distinct energy levels. They are responsible for chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of elements.
Complete the Table for Key Subatomic Particles
| Name | Symbol | Charge | Mass (amu) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | p | +1 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Neutron | n | 0 | 1 | Nucleus |
| Electron | e– | -1 | 0.00055 | Energy levels around the nucleus |
Comparison of Key Subatomic Particles: Complete The Following Table For The Three Key Subatomic Particles
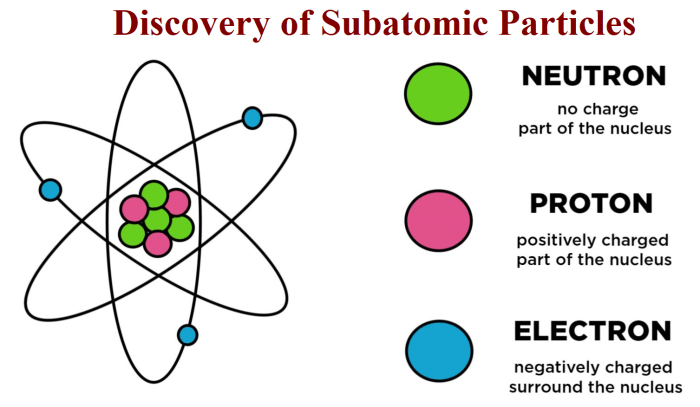
Protons, neutrons, and electrons exhibit distinct differences in their properties, which determine their unique roles in the atom.
- Charge:Protons carry a positive charge, electrons carry a negative charge, while neutrons are neutral.
- Mass:Protons and neutrons have approximately equal masses of 1 amu, while electrons have a much smaller mass of approximately 0.00055 amu.
- Location:Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels.
These differences in properties contribute to the unique roles of each particle in the atom. Protons determine the atomic number and contribute to the mass, while neutrons contribute to the mass but have no net charge. Electrons, on the other hand, are responsible for chemical bonding and determine the chemical properties of elements.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of the charge of subatomic particles?
The charge of subatomic particles determines their interactions with each other and with external electric and magnetic fields. It plays a crucial role in shaping the structure and properties of atoms and molecules.
How does the mass of subatomic particles affect their behavior?
The mass of subatomic particles influences their inertia and their participation in nuclear reactions. It is a fundamental property that contributes to the stability and dynamics of atomic nuclei.
Where are subatomic particles located within an atom?
Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons occupy orbitals surrounding the nucleus. This arrangement determines the overall structure and properties of the atom.